The BIANCA Box
Innovation in the field of Personal Protective Equipment
Alphainfluenzavirus Influenza A virus
Influenza (Seasonal Flu)
Media & Press
The latest articles, news, and opinions on a range of subjects from the spread of airborne pathogens to innovations in personal protective equipment, pandemic projections, and more. Perfect for medical professionals and anyone wanting to learn more about these trending healthcare topics.
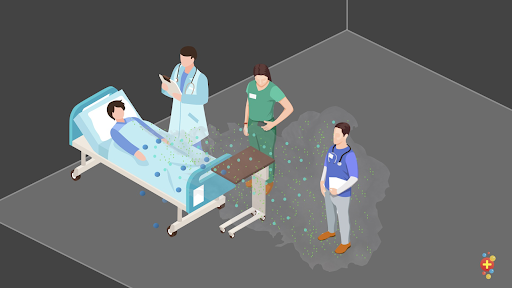
AEROSOL GENERATING PROCEDURES (AGP)
Andrew Tagg is an Emergency Physician who defines what an aerosol generating procedure (AGP) is and discusses how they increase the spread of a pathogen when healthcare workers perform various treatment modalities for pediatric patients, which also applies for adults..
“As more cases of Covid19 present to health care facilities across the world, there seems to be some confusion as to what is an aerosol-generating procedure. Turning up to work is not without risk with a large number of healthcare workers in Italy and Ireland diagnosed with COVID19.”

Covid was third-leading cause of death in U.S. once again in 2021
CDC reports examine U.S. Death Rates for 2021 and found that it was responsible for 13% of all deaths in the U.S. in 2021, up from 10 percent the year prior.
“In both 2020 and 2021, the only conditions that killed more people than Covid were heart disease, which caused 693,000 deaths last year, and cancer, at 605,000 deaths in 2021.”

‘It doesn’t feel worth it’: Covid-19 is pushing New York’s EMTs to the brink
Emergency Medical Service (EMS) workers are overworked and underpaid, all while risking their lives to save the lives of others.
“Nationwide, at least 128 medical first responders have died of Covid-19, according to Lost on the Frontline, a Guardian/Kaiser Health News investigation.”

COVID-19: Estimated 115,000 healthcare workers have died from disease, says WHO
Healthcare workers worldwide have become collateral damage as we wage this war against the coronavirus.
“Many have themselves become infected, and while reporting is scant, we estimate that at least 115,000 health and care workers have paid the ultimate price in the service of others.”

Lost on the frontline – Thousands of US healthcare workers died fighting Covid-19 in the first year of the pandemic. We counted them and investigated why.
3,607 US healthcare workers have died from January 2020 – April 2021
“‘Lost on the Frontline,’ an ongoing project from The Guardian and Kaiser Health News that aims to document the lives of health care workers in the U.S. who die from COVID-19, and to investigate why so many are victims of the disease. If you have a colleague or loved one we should include, please share their story.”

COVID-19: Health worker death toll rises to at least 17,000 as organizations call for rapid vaccine rollout
One healthcare worker was dying every 30 minutes during the pandemic
“For one health worker to die from COVID-19 every 30 minutes is both a tragedy and an injustice. Health workers all over the world have put their lives on the line to try and keep people safe from COVID-19, yet far too many have been left unprotected and paid the ultimate price,” said Steve Cockburn, Head of Economic and Social Justice at Amnesty International.
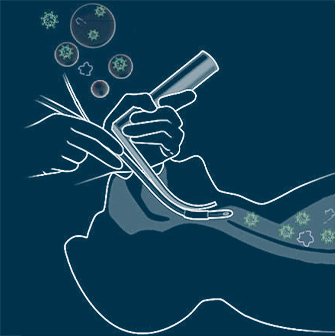
What Is an Aerosol-Generating Procedure?
“The World Health Organization stipulates that intubation, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheotomy, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, bronchoscopy, and sputum induction are definite aerosol-generating procedures because epidemiologic studies have associated these procedures with greater risk for health care worker infections.”
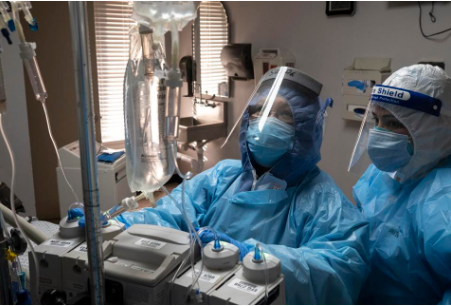
Nearly 300,000 Healthcare Workers Have Been Infected With Covid-19 Worldwide, Threatening Health Systems
With over 300,000 healthcare workers infected with COVID-19, healthcare systems worldwide were collapsing when the pandemic hit.
“Of the thirty-seven countries surveyed, the United States had the highest number of coronavirus infections among healthcare workers with 114,500 infections reported as of August 15th. Mexico followed with a reported 78,200 infections while France and Italy had 30,000 and 29,000 coronavirus infections respectively.”
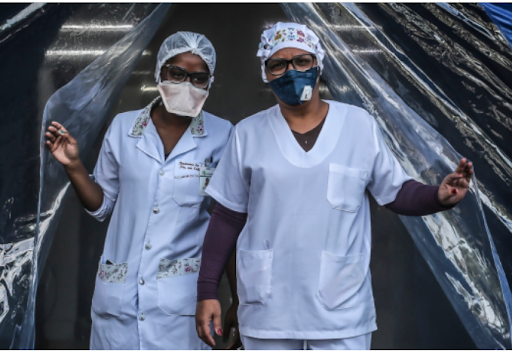
Global: Health workers silenced, exposed and attacked
Amnesty International researchers surveyed 31 countries and found recorded reports of strikes, threatened strikes, or protests, by healthcare and essential workers as a result of unsafe working conditions.
“Alarmingly, Amnesty International documented cases where health workers who raise safety concerns in the context of the COVID-19 response have faced retaliation, ranging from arrest and detention to threats and dismissal.”
Invest in preventing the next outbreak and commit to protecting our first responders.
PREVENT ANOTHER OUTBREAK
Respiratory Epidemics and Pandemics
Pandemics have been well documented throughout history, with mention of the first alpha coronavirus as far back as the 1200-1500s. To prevent loss of life in the future, we must continue to learn from the past.